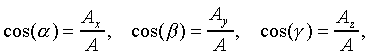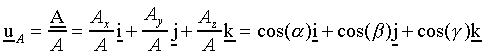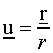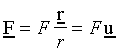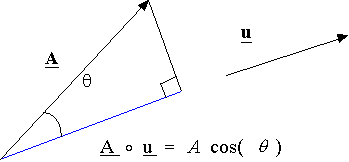Vectors in 3-D
Unit vector: A vector of unit length.
Base vectors for a rectangular coordinate system: A set of three mutually orthogonal unit vectors
Right handed system: A coordinate system represented by base vectors which follow the right-hand rule.
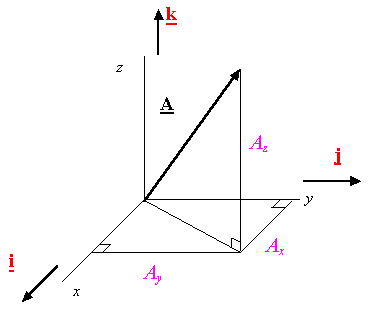
Rectangular component of a Vector: The projections of vector A along the x, y, and z directions are Ax, Ay, and Az, respectively.
Magnitude of a Vector:
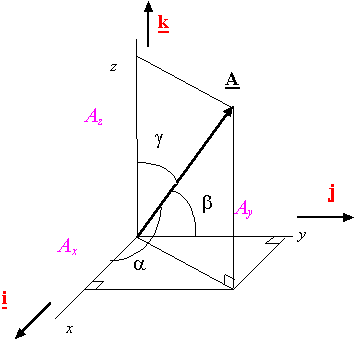
Direction Cosines: Cos(a), Cos(b),
Cos(g)
Unit vector along a vector: The unit vector uA along the vector A is obtained from
Addition of vectors: The resultant vector FR obtained from the addition of vectors F1, F2, …, Fn is given by
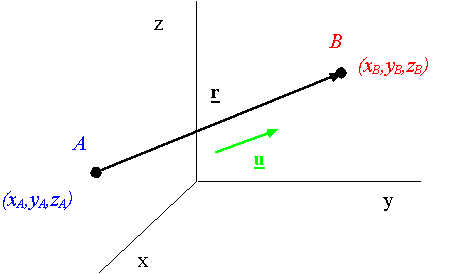
Coordinates of points in space: The triplet (x,y,z) describes the coordinates of a point.
The vector connecting two points: The vector connecting point A to point B is given by
A unit vector along the line A-B: A unit vector along the line A-B is obtained from
A vector along A-B: A vector F along the line A-B and of magnitude F can be obtained from
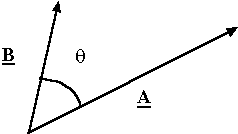
The dot product: The dot product of vectors A and B is given by
Projection of a vector by using the dot product: The projection of vector A along the unit vector u is given by
Examples: