Notation, Units, and Rounding Numbers
Notation:
|
|
Book
|
By hand
|
|
Scalar |
a |
a |
|
Vector |
a (bold faced) |
a or |
Units:
|
|
|
SI |
|
U.S. |
|
|
Mass |
M |
kilogram |
kg |
slug |
|
|
Length |
L |
meter |
m |
feet |
ft |
|
Force |
F |
Newton |
N |
pound |
lb |
|
Time |
T |
second |
s |
second |
sec |
Relation
between units is based on the equation F=ma:
1 N = (1 kg) (1 m/s2)
1
lb= (1 slug) (1 ft/sec2 )
Example
of calculating mass in U.S. system: The mass, m, of a particle which weighs
W=10 lb and is in a gravitational field of with an acceleration of gravity
g=32.2 ft/sec2 is
![]()
Unit
conversion:
|
l lb |
= |
4.4482 N |
|
1 slug |
= |
14.5938 kg |
|
1 ft |
= |
0.3048 m |
|
1 ft |
= |
12 in |
|
1 mile |
= |
5,280 ft |
|
1 kip |
= |
1,000 lb |
|
1 ton |
=
|
2,000 lb |
Rounding
numbers:
Round your final answers to 3
significant figures
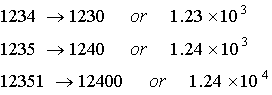
Check
equations by checking that all terms in an equation have the same dimensions
![]()
ã Mehrdad Negahban and the
University of Nebraska, 1999-2000.
All
rights reserved
Copy
and distribute freely for personal use only
Department
of Engineering Mechanics, University of Nebraska, Lincoln, NE 68588-0526