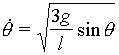
EXAMPLE 2: Euler's 2nd law for 2-D motion
The uniform bar of mass m and length l† is released from rest in the horizontal position. Calculate the equation of its angular velocity as a function of the angle of rotation.
Solution:
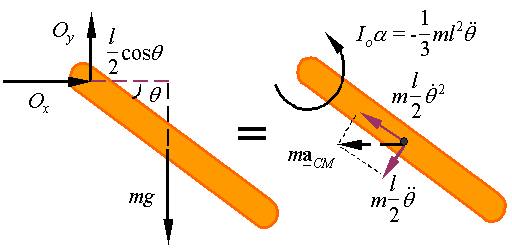
Since O is a fixed point we can use the special form of Eulerís second law for rotation about fixed points.
![]()
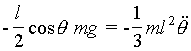
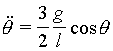
This
is the equation of motion for the bar. We must integrate it to get the angular
velocity ![]() .
.
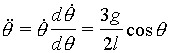
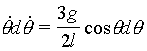
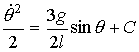
The
constant of integration C is evaluated using the initial condition ![]()
at ![]() †to give C=0.
Therefore,
†to give C=0.
Therefore,