GEOMETRY
Areas of focus:
- Area and perimeter of basic two-dimensional objects: triangles, rectangles, circles, trapezoids, parallelograms, and ellipses
- Volume and surface area of three-dimensional objects: cubes, spheres, parallelepipeds, ellipsoids, and cones
- Relation among angles when lines intersect
- Relation among angles when parallel lines intersect a line
- Relations between angle of a triangle
- Similar triangles
- Pythagorean theorem
- Pythagorean triplets
- Centroid of geometric objects
- Approximation of area and volume
Area and
perimeter of basic two-dimensional objects:
The following is a listing of the area and/or perimeter of a triangle, rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, circle, sector of a circle, and ellipse.
Triangle:
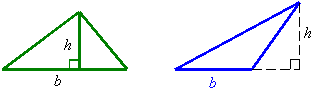
b = base
h = height
![]()
Rectangle/Square:
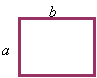
Area = a b
Perimeter = 2 (a + b)
Parallelogram:
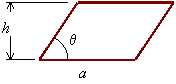
Area = a h
Perimeter = ![]()
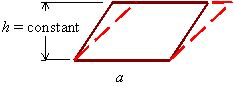 Area = constant for
parallelograms with equal base and equal height.
Area = constant for
parallelograms with equal base and equal height.
Trapezoid:
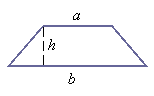
![]()
Circle:
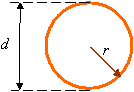
r = radius
d = diameter =2r
Area =![]()
Circumference = ![]()
![]()
Sectors of a circles:
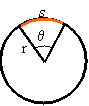
Arc Length, ![]()
Angle measured in radians, ![]()
Sector area =![]()
Ellipses:
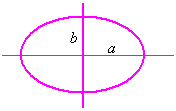
![]()
Volume
and surface area of three-dimensional objects:
The following is a listing of the surface area and/or volume of a cube, parallelepiped, cylinder, sphere, cone, and pyramid.
Cubes and rectangular parallelepipeds:
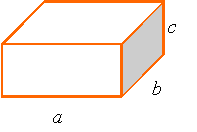
Volume = abc
Surface area = 2(ab+bc+ca)
Parallelepipeds:
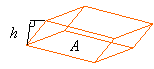
A = Area of base
h = Height
Volume = Ah
Right Circular Cylinder:
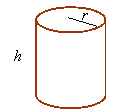
Volume
= ![]()
Lateral surface =![]()
Spheres:
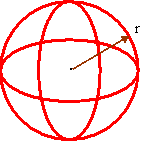
r = radius
![]()
![]()
Cones:
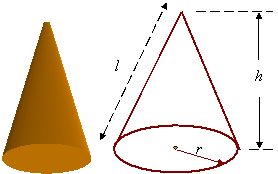
![]()
![]()
l2 = r2 + h2
Pyramid or irregular cone:
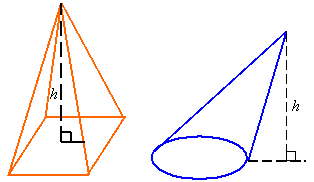
![]()
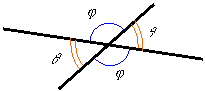
Relation
among angles when lines intersect:
Opposing angles are equal when two straight lines intersect, and adjacent
angles add to 180o (i.e., ![]() ).
).
Relation
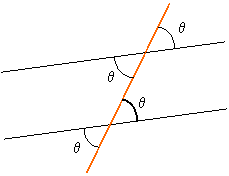
among angles when parallel lines intersect a line:
When a line intersects parallel lines it makes identical angles with both lines.
Relations
between angle of basic objects:
Interior angles of a triangle:
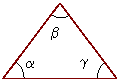
![]()
Exterior angles of a triangle:
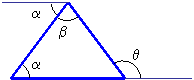
![]()
Interior angels of a parallelogram:
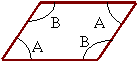
In a parallelogram opposite angles are equal
Also: 2A + 2B =360o
The triangles ABC and ADE are called similar triangles. The sides of two similar triangles are proportional and the angels are the same. The respective heights of these triangles are also proportional to the sides.
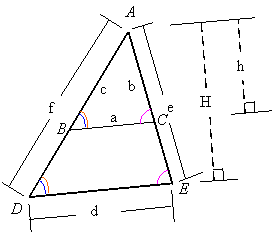
![]()
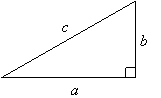
The Pythagorean theorem states that for a right triangle, as shown, there exists a relation between the length of the sides given by
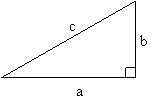
a2 + b2
= c2
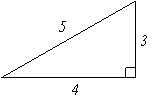
There are Pythagorean triples for the sides a, b, and c of a right triangle. The triplets (a,b,c) are related through the relation a2 + b2 = c2, such as (3,4,5), (5,12,13) and (7,24,25). All constant multiples of these triplets (e.g., (6,8,10) from (3,4,5)) also create Pythagorean triplets. The following are examples of right triangles with sides given in terms of Pythagorean triplets.
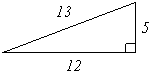
Centroid of
geometric objects:
The centroid of an object is the geometric center of it. The centroid of the following objects are indicated by a C.
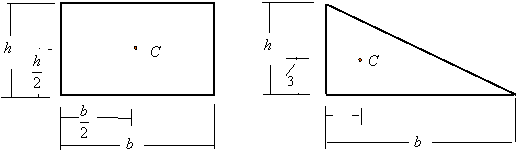
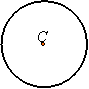
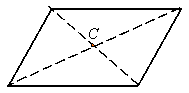
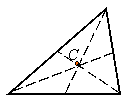
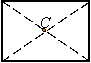
Approximation
of area and volume:
Strips:
The area of a strip can be approximated as the length of the strip times its width if the strip is of uniform width and if its width is small compared to its length.
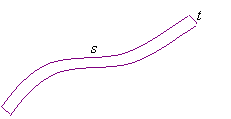
s = length
t = width
![]()
Slabs and shells:

The volume of a slab can be calculated as the surface area times the thickness if the thickness is uniform. The volume of a shell can be approximated using this relation, but the thickness must be small relative to the principal radii of curvature of the shell.
A = surface area
t = thickness
Volume = At